

If you have surgery, it may be difficult to move around as much as you would normally at first. This means they’re not as physically active. Being less active due to treatmentįor some people, their breast cancer treatment can make them feel very tired and weak, or cause some muscle and joint pain. If this does happen the line may need to be removed.

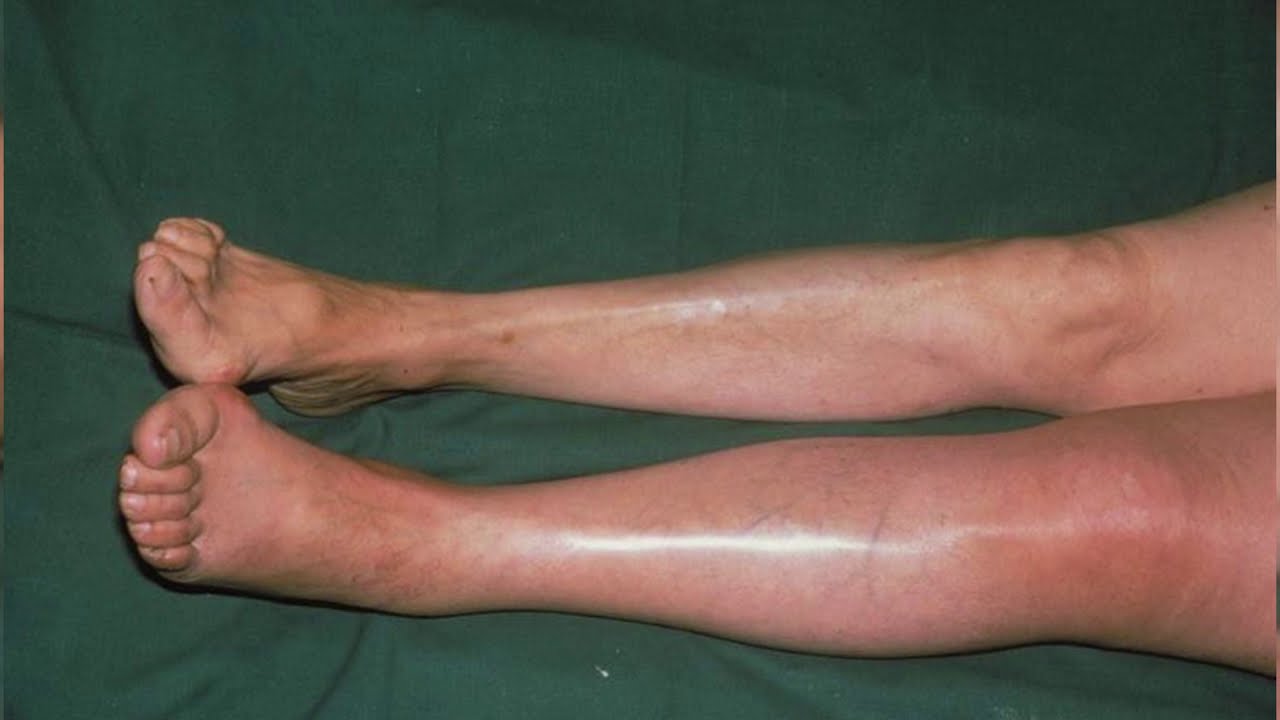
If you have a central line, such as a Hickman line, PICC line or port, it’s possible for a blood clot to form in a vein at the end of the line. Blood samples can also be taken from a central line. Having a central lineĪ central line is a tube that’s inserted into a large vein and can be used to give chemotherapy or other drugs. If you’re due to have surgery or chemotherapy let your treatment team know if you have a previous history of blood clots. Hormone therapies such as tamoxifen and fulvestrantīoth surgery and chemotherapy can damage the walls of blood vessels, which can increase the risk of a blood clot developing.Targeted therapies such as palbociclib and trastuzumab emtansine.Chemotherapy – as cells are destroyed by chemotherapy they can release substances that cause blood clots.Surgery – the risk of developing blood clots is highest 2–10 days after surgery and remains higher than normal for up to 90 days.Some treatments for breast cancer may increase the risk of developing a blood clot. 4. Breast cancer treatments that increase the risk of blood clots This means a blood clot may be more likely to form, particularly if the cancer affects the liver. Some people with cancer may also have lower levels of proteins in the blood that help to keep it thinned. Having higher than normal amounts of platelets and clotting factors in the body means the blood is more likely to clot. These play a role in helping the blood to clot and stop any bleeding. This is because cancer releases a higher number of platelets and clotting factors. People with breast cancer have a higher risk of blood clots than those without cancer. 3. The risk of blood clots in people with breast cancer If a blood clot travels to the lungs it is known as a pulmonary embolism (PE). This can be harmful because it stops blood flow to parts of the body. If a blood clot breaks away from the DVT and travels to another part of the body it can block a blood vessel. If you have an injury your blood will clot to reduce bleeding.īut there are times when blood clots can be harmful and need treatment.ĭeep vein thrombosis (DVT) is when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually the leg. Swelling, redness or tenderness where a central line is inserted to give chemotherapy, for example in the arm, chest area or up into the neckīlood clots can naturally happen quite often.Pain, redness/discolouration, heat and swelling of the arm or leg.If you experience any of the following symptoms contact your treatment team or go to your local A&E department straight away: If you develop a blood clot during treatment, your treatment may be paused until the blood clot has been treated. If the cancer has spread to other parts of the body ( secondary breast cancer), this can also increase the risk.īlood clots can be harmful but are treatable so it’s important to report symptoms as soon as possible. Their risk is higher because of the cancer itself and some treatments for breast cancer. People with breast cancer have a higher risk of blood clots. Further support 1. Breast cancer and blood clots Other factors that can increase the risk of blood clotsĩ. Breast cancer treatments that increase the risk of blood clotsĥ. The risk of blood clots in people with breast cancerĤ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
